Now that we have Jupyter Notebooks with C# installed, using it as an environment to play with SQLite is very easy. SQLite is a relational database that is small in footprint and self-contained. It also has a great in-memory mode which is perfect for playing around in a Jupyter notebook.
You can access my SQLite example notebook here.
You can now launch this online and follow along:
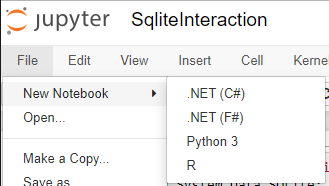
You can create a C# Notebook from the file menu of Jupyter.
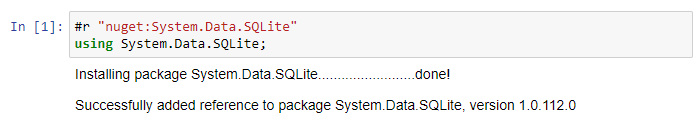
We need to pull in the nuget package System.Data.SQLite to interact with the database.
#r "nuget:System.Data.SQLite"
using System.Data.SQLite;
#r is used to reference a dll or a nuget package. If you prefix the command with "nuget:" then the jupyter notebook will download the nuget and add it as a reference. Then as in usual c#, you must reference it.
When you run this cell, you should see the following output:
We can then create a connection to an in-memory SQLite database.
SQLiteConnection conn;
conn = new SQLiteConnection("Data Source=:memory:;Version=3;New=True;");
try
{
conn.Open();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
Creating two identical tables SampleTable and SampleTable1.
using (SQLiteCommand sqlite_cmd = conn.CreateCommand()) {
string Createsql = "CREATE TABLE SampleTable(Col1 VARCHAR(20), Col2 INT)";
string Createsql1 = "CREATE TABLE SampleTable1(Col1 VARCHAR(20), Col2 INT)";
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = Createsql;
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = Createsql1;
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
Inserting a set of data into these tables.
using (SQLiteCommand sqlite_cmd = conn.CreateCommand()) {
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SampleTable(Col1, Col2) VALUES ('Test Text ', 1);";
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SampleTable(Col1, Col2) VALUES ('Test1 Text1 ', 2);";
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SampleTable(Col1, Col2) VALUES ('Test2 Text2 ', 3);";
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SampleTable1(Col1, Col2) VALUES ('Test3 Text3 ', 3);";
sqlite_cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
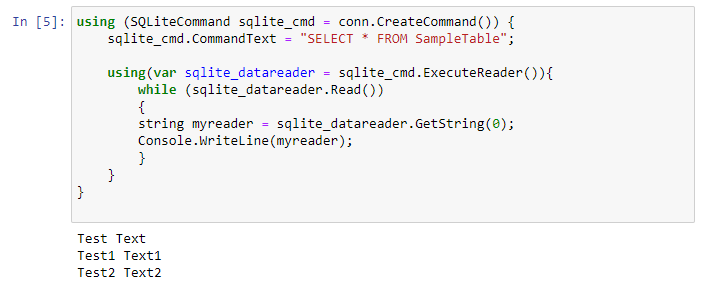
Reading from SampleTable to verify the insertions went through correctly.
using (SQLiteCommand sqlite_cmd = conn.CreateCommand()) {
sqlite_cmd.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM SampleTable";
using(var sqlite_datareader = sqlite_cmd.ExecuteReader()){
while (sqlite_datareader.Read())
{
string myreader = sqlite_datareader.GetString(0);
Console.WriteLine(myreader);
}
}
}
If you executed the whole workbook up to now, you should have the following output.
Closing the connection to the databse.
conn.Close();